Test
{{#images:version650-32x32.png|stock}}
Les vues locales sont des type de données vues déclarées localement à l'intérieur d'une opération.
Par exemple le code suivant déclare une vue MyView et effectue une recherche sur cette vue :
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) unCode:string = unCodeA; unEntier:Integer = refB.unEntierB; end;
var inst:MyView; begin
inst := MyView.Find('unCode=%1',,true,['B1']);
if Assigned(inst) then
begin
...
end;
end </source>
Le périmètre du type est limité à la procédure, il n'est donc pas possible de passer les objets de la vue en paramètre à d'autres fonctions (pour cela utilisez une vue globale).
La syntaxe pour définir une vue locale :
BNF style grammar :
<nom_vue> ::= ViewOf(<class_dec>) [<attributes>] end
<class_dec> ::= <class_names> | <class_name> <class_dec>
<class_names> ::= <class_name>| [<class_name> ,]
<class_name> ::= identifier
<class_dec> ::= distinct
<attributes> ::= <attribute_def> | <attribute_def> <where_def>
<attribute_def> ::= <simple_attribute_def> | <simple_attribute_def> <attribute_directive>
<simple_attribute_def> ::= <attribute_dec> | <attribute_dec> = <attribute_ref>
<attribute_dec> ::= <attribute_name> : <type_name>
<attribute_ref> ::= <main_class_attribute_name> | <operator>(<main_class_attribute_name>)
<operator> ::= <aggregate_operator> | <date_operator> | <join_operator>
<aggregate_operator> ::= count|sum|max|min
<date_operator> ::= year|month|quarter|week|day|dayofyear|dayofweek|hour|minute|second
<join_operator> ::= join
<attribute_directive> ::= primary | orderby | orderby desc | over | notInSelect
<where_def> ::= [ <expression> ]
Type
NomDeVue = ViewOf(NomDeClassePrincipale)
Attribut : Type;
Attribut : Type = AliasDe;
Attribut : Type = operator(AliasDe);
Attribut : Type = AliasDe primary;
Attribut : Type = AliasDe orderby;
Attribut : Type = AliasDe orderby desc;
[ expression ]
end;
Les vues peuvent utiles pour effectuer des traitement sur des classes complexes, par exemples :
Exemples
Curseur sur une classe vue
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) newCode:string; unCode:string = unCodeA; unEntier:Integer = refB.unEntierB; end;
var inst:MyView; cursor:MyViewCursor begin
Result := 0;
cursor := MyView.CreateCursorWhere(unCode=%1,',true,[S]);
foreach inst in cursor do
begin
Result := Result + inst.unEntier;
end;
end; </source>
Vue avec jointure externe
<source lang="delphi"> function ViewExternalJoin(const S:string):Boolean; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) newCode:string; unCodeAA:string = unCodeA; unCodeBB:string = refB+unCodeB; end;
var inst:MyView; begin
inst := MyView.Find('unCodeAA=%1',,true,[S]);
if Assigned(inst) and (inst.unCodeAA=S)
then Result := True
else Result := False;
end;
</source>
Vue sur une interface
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(InterfaceA, ClassA1, ClassA2) unCode:string = unCodeA primary; .... end;
begin
...
end; </source>
Vue sur des combinaisons uniques d'attributs
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA distinct) unCode:string = unCodeA primary; unEntier:Integer = refB.unEntierB; end;
begin
...
end; </source>
Vue avec agrégats
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) unCode:string = unCodeA primary; unEntier:Integer = sum(unEntier); end;
begin
...
end; </source>
Vue avec agrégats sur un montant
<source lang="delphi"> Type
myView = viewof(WFClasseX) mysum:TMoney = sum(credit) orderby; end;
var sel:TSelector; inst:MyView; S,stag:string; begin
sel := MyView.CreateSelector(,,true,[]);
S := ; stag := ;
foreach inst in Sel.AsCursor do
begin
S := S+stag+Formatfloat('0.00',inst.mysum.Value);
stag := ',';
end;
showmessage(S);
Result := FALSE;
end; </source>
select sum(t0.credit) "mysum",t0.credit_CodeDevise "mysum_CodeDevise" from dbo.WFCLASSEX t0 group by t0.credit_CodeDevise order by sum(t0.credit)
Vue avec agrégats sur un attribut enfant
<source lang="delphi"> Type
myView = viewof(WFClasseX) mysum:TMoney = sum(credit:TCValue) orderby; end;
begin
...
end; </source>
select sum(t0.credit_TCValue) "mysum" from dbo.WFCLASSEX t0 order by sum(t0.credit_TCValue)
Vue avec un opérateur de date
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassC distinct) unCode:string = unCodeC primary; unMois:Integer = month(uneDate); end;
begin
...
end; </source>
Vue avec un opérateur de date (diff)
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(iDayDiff):string; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassC distinct) unCode:string = unCodeC primary; DayDiff:Integer = DayDiff(uneDateStart,uneDateEnd); end;
begin
inst := MyView.Find('DayDiff >= %1',,true,[iDayDiff]);
if Assigned(inst)
then Result := inst.unCode
else Result := 'Not found';
end; </source>
Vue avec référence
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) unCodeAA:string = unCodeA; refB:reference = refB; end;
begin
...
end; </source>
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) unCodeAA:string = unCodeA; refB:ClassB = refB; end;
begin
...
end; </source>
Vue avec variable référence
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) unCodeAA:string = unCodeA; refB:ClassB; end;
begin
...
end; </source>
Vue avec filtre
<source lang="delphi"> function foo(const S:string):Integer; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassA) unCodeAA:string = unCodeA; unCodeBB:string = refB.unCodeB; [ unCodeA='A1' ] end;
begin
...
end; </source>
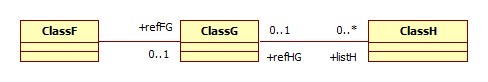
Vue avec traversée de liste
<source lang="delphi"> function _Concat(const S:string):string; Type
MyView = viewof(ClassF) unCodeF:string = unCodeF; unCodeG:string = refFG.unCodeG; unCodeH:string = refFG.listH.unCodeH; end;
var ls:MyViewList; stag:string; idx:integer; begin
ls := MyView.CreateListWhere('unCodeG=%1',,'unCodeH',true,-1,[S]);
Result := ; stag := ;
for idx:=0 to ls.Count-1 do
begin
Result := Result+stag+ls.Refs[idx].unCodeH;
stag := ',';
end;
end; </source>
Vue avec jointure sur une classe
Type
myView = class(myClass)
vp1:joinClass1 = join(A,B);
vp2:JoinClass2 = join(A,B,W);
vp3:JoinClass3 = join(W);
....
end;
| Paramètre | Usage |
|---|---|
| A | Attribut de la classe join (joinClass) |
| B | Chemin à partir de la classe base (myView) |
| W | Clause Where sur la classe join |
La clause Where peut être exprimée avec les préfixes :
| self | Préfixe de la classe de base |
| ? | Préfixe de la classe Join |
| xx | alias d'une jointure de classe |
| Tip : Il est possible de créer un produit cartésien entre deux classes en utilisant une jointure avec une clause where toujours vraie. |
<source lang="delphi"> //Procedure expensePendings(req:Tjson; var res:TObject); Type
ExpenseView = viewOf(TNoteFrais) vp: TValideurPossible = join(ValidationEtat.EtatPossible.EtatMetier, EtatNF); aManager:string = vp.ContactEtablissement.oidutilisateur; // aDate:TDatetime = nDate; aRef:string = referencePiece; aReason:string = Caption; aAmountOrg:TMoney = MontantTTC; aAmountAct:TMoney = MontantRetenu; aQuantity:TQuantity = Quantite; aUser:string = Salarie.Operateur.oidutilisateur; aType:string = FraisSalarie.Caption; aMode:Integer = FraisSalarie.modeRemboursement; aAmountMax:TMoney = FraisSalarie.montantPlafond; aStatus:Integer = Statut; end;
var json:TJson; ls:TSelector; indx,ctn:Integer; inst:ExpenseView;
AWhere,AOrder:string; Args:Array[0..5] of variant;
begin
json := TJson.Create(); res := json; // AWhere := '(aManager=%1) and (aStatus=%2)'; Args[0] := GlbUserName; Args[1] := StatutNF_AValider; AOrder := 'aUser,-aDate';
indx := 0; ctn := 0;
ls := ExpenseView.CreateSelector(AWhere,AOrder,true,Args);
foreachP inst in ls.AsCursor do
begin
. . .
end;
end; </source>
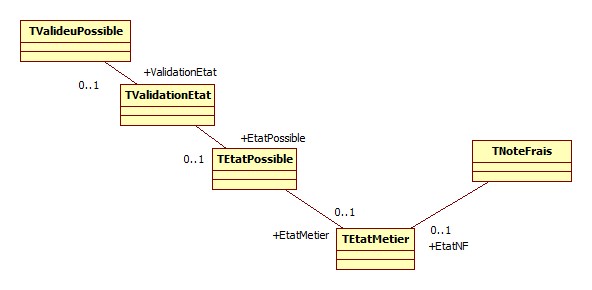
Dans cet exemple le modèle est celui-ci :
La classe TEtatMetier est atteinte par deux chemins différents, un issu de la classe TValideurPossible et un issu de la classe TNoteFrais. La jointure est réalisée sur l'objet TEtatMetier.
vp: TValideurPossible = join(ValidationEtat.EtatPossible.EtatMetier, EtatNF);
- TValideurPossible est la classe qui va être jointe
- vp défini un alias sur cette classe qui peut être ensuite utilisé dans la définition de la vue.
- ValidationEtat.EtatPossible.EtatMetier est le chemin issu de la classe jointe
- EtatNF est le chemin issu de la classe de la vue.
Exemple, vue locale avec produit cartésien, jointure par clause where et sous requêtes
<source lang="delphi"> //procedure RubriqueParExerciceDetail; Type
vueSolde = viewof(TCumulPeriodeCompte) codeCompte:string = CompteGeneral.codeCompte; datePeriode:TDatetime = Periode.dateDebut; value:Currency = sumDiff(debitTenue,creditTenue); oidExercice:TOID = Periode.oidexercice; [(typeLot=1)] end;
vueSelection = viewOf(TSelectionCompte)
vc:TCompteGeneral = join('(codeCompte>=self.compteInferieur) and (codeCompte<=self.compteSuperieur)');
vp:TPeriode = join('(1=1)');
ve:TExercice = join(oid,vp.oidexercice);
ve1:TExercice = join('(?.dateDebut = DateAdd(dpyear,ve.dateDebut,-1))');
//
idCompteGeneral:TOID = vc.oid primary;
idRubrique:TOID = oidRubriqueCompte primary;
idPeriode:TOID = vp.oid primary;
idExercice:TOID = vp.oidexercice;
idExerciceN1:TOID = ve1.oid;
//
codeRubrique:string = RubriqueCompte.code orderby;
libelleRubrique:string = RubriqueCompte.Caption;
codeCompte:string = vc.codeCompte orderby;
libelleCompte:string = vc.Caption;
libellePeriode:string = vp.Caption;
//
datePeriode:TDatetime = vp.dateDebut orderby desc;
year:Integer = year(vp.dateDebut);
month:Integer = month(vp.dateDebut);
valueN0:currency = VueSolde.select('value','(oidExercice=self.idExercice) and (codeCompte=self.codeCompte) and (datePeriode<=self.datePeriode)',,true,[]);
valueN1:currency = VueSolde.select('value','(oidExercice=self.idExerciceN1) and (codeCompte=self.codeCompte) and (datePeriode<=DateAdd(dpYear,self.datePeriode,-1))',,true,[]);
end;
var Sel:TSelector; inst:vueSelection; S,stag:string; begin
Sel := vueSelection.CreateSelector('(codeRubrique=%1) and (year=2022) and (month=3)',,True,['SIG.L02']);
S := ; stag := ;
forEach inst in Sel.AsCursor do
begin
S := S+stag+inst.codeCompte;
stag := ',';
end;
showMessage(S);
end; </source>
| Tip : Notez l'opérateur SQL DateAdd() qui peut être utilisé dans la partie littérale d'une expression |
Vue avec jointures liées
<source lang="delphi">
Type VueValideur = viewOf(TPieceTaxable) vp1: TValideurPossible = join(ValidationEtat.EtatPossible.EtatMetier,EtatMetier); vp2: TValideurPossible = join(ValidationEtat.RegleValidation,RegleValidation); gcv: TGroupeContactValidation = leftjoin(TGroupeValidation,vp2.ContactEtablissement); aId1:TOID = vp1.oid; aId2:TOID = vp2.oid; // ... [ (aId1=aId2) and ... ] end;
</source>
Dans cet exemple :
- vp1 et vp2 sont deux jointures qui coincident sur le même tuple.
- La coincidence des deux jointures est réalisée par le clause where (aId1=aId2)
- gcv est une jointure sur le tuple défini par vp1 et vp2
Voir aussi :